Gone are the days of firefighting after breakdowns. What once seemed futuristic is now the baseline expectation for manufacturers that aim to compete globally. In an era of razor-thin margins and relentless pressure to reduce downtime, smart asset maintenance will no longer be optional; it will be mission-critical.
As we look ahead to 2026, the manufacturing sector faces new challenges: an aging workforce, sustainability pressures, supply chain fragility, and the adoption of agentic artificial intelligence (AI). At Ultimo, we see these forces converging on the maintenance function, and we have four bold predictions for how asset maintenance will evolve. More than that, we believe this evolution must be mapped against a maturity framework so organizations can chart where they stand and where to go next.
1: Digital Labor Joins the Maintenance Workforce
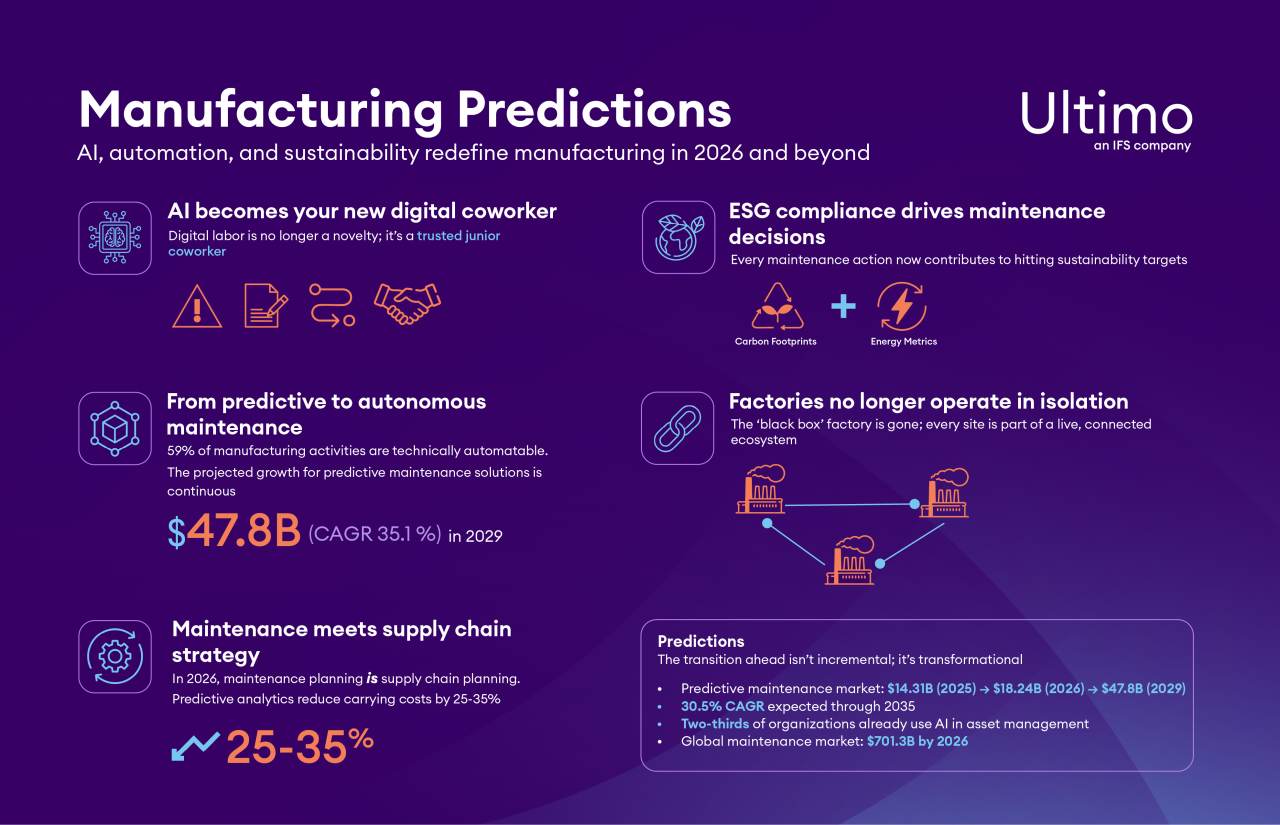
Last year’s forecast of workforce transformation is now reality. As we move through 2026, “digital labor” will no longer be a novelty; it will be a trusted junior coworker. As senior maintenance engineers retire or depart, the dissolution of tribal knowledge willleave gaps. Digital labor (agentic AI assistants) will step in to fill those gaps.
These AI agents will assist with routing work orders, diagnosing faults, creating root-cause templates, reporting safety incidents or near-misses and even onboarding new technicians. They will evolve through supervised learning and reinforcement from human guidance, becoming ever more capable. The burden of administrative overhead will shrink, allowing human expertise to focus on higher-value tasks.
By augmenting maintenance teams with agentic assistance, manufacturers will close skill gaps faster and protect institutional knowledge from walking out the door.
2: AI-Powered Autonomous Maintenance Operations
The AI-powered predictive maintenance of 2025 has advanced into autonomous operations. By 2026, it’s not unreasonable to expect leading manufacturers to be automating 40–60 percent of routine maintenance tasks end-to-end. This shift will be powered by predictive maintenance platforms, digital twins of production lines, and the rise of agentic AI.
AI systems will autonomously handle scheduling, spare parts management, technician dispatch, and optimization of maintenance windows to minimize production disruptions. Machine learning models trained on aggregated manufacturing data will identify failure patterns across sites and asset types, accelerating anomaly detection and resolution.
Digital twins will play a central role: each line or cell will maintain a live model simulating wear, predicting failure progression, and weighing maintenance trade-offs. These twins will ingest sensor data, control-system signals, and site-wide trends to guide precisely timed interventions.
Market signals confirm this trajectory. McKinsey estimates that 59 percent of manufacturing activities can be automated today. The predictive maintenance market is forecast to grow from $10.6 billion in 2024 to $47.8 billion by 2029. Gartner predicts that agentic AI will become a standard feature of industrial operations by the late 2020s.
Early adopters are already seeing results: numerous case studies show that AI-driven predictive maintenance has reduced downtime by 20–50 percent compared to reactive approaches, while also improving safety and lowering costs.
3: Supply Chain Resilience & Smart Inventory Management
In 2025, the focus was on cybersecurity and digital supply chain visibility. By 2026, maintenance planning and supply chain strategy are fully intertwined. The shock of global supply chain disruptions has taught manufacturers not to rely on distant suppliers for every critical spare. Instead, manufacturers will use AI-powered risk models to identify which spares are truly mission-critical and where to localize manufacturing via 3D printing or on-site microfactories.
Predictive analytics will optimize spare parts across sites, shrinking stock depreciation while preventing dangerous shortages. A study by IDC Manufacturing Insights found that many organizations expect carrying costs to fall by 25–35 percent through smarter inventory orchestration.
To hedge against risk, real-time geopolitical and logistics data will drive strategic stockpiling and supplier diversification. In effect, maintenance planning will become supply chain planning.
4: Sustainability-Driven Asset Lifecycle Optimization
The sustainability pressures flagged in 2025 are no longer optional. Through 2026, carbon footprint and energy efficiency will become central criteria in asset maintenance decisions. Repair vs. replace trade-offs will incorporate embedded carbon footprint, energy use, and environmental compliance metrics.
Every maintenance action will embed energy monitoring and optimize for minimal waste. Rehabilitation, refurbishment, and component reuse will become more prevalent, following circular manufacturing principles. Compliance with emissions and environmental reporting will be automated and integrated within maintenance workflows.
In highly regulated markets, this will not be discretionary: regulators and investors will demand lifecycle transparency. Maintenance will become one of the levers for hitting broader ESG targets.
5: Hyper-Connected Manufacturing Ecosystems
Where 2025 emphasized advancing digitalization, 2026 delivers on its promise. In the coming year the “black box” factory no longer exists. Manufacturers and suppliers will operate within shared, real-time performance ecosystems. Asset health data will flow across value chains, enabling collaborative optimization – market-wide benchmarking, dynamic scheduling, and cross-plant planning.
Standardized asset data protocols will emerge, enabling cross-facility interoperability. Planning systems will dynamically shift production based on asset health across regional hubs.
Grounding the Predictions: Market & Tech Trends
The predictive maintenance market alone is projected to grow from $14.31 billion in 2025 to $8.24 billion in 2026, with a 30.5 percent CAGR expected through 2035.
Another estimate sees the global predictive maintenance market reaching $47.8 billion by 2029 (starting from $10.6 billion in 2024).
The broader maintenance market is also growing: the global maintenance market is predicted to hit $701.3 billion by 2026.
According to recent studies, two-thirds of organizations already report having implemented AI in their asset management practices.
These numbers confirm that the transition ahead is not incremental, it’s transformational.
Deploying advanced maintenance technologies is not a silver bullet. Success requires alignment of people, processes, and systems. That’s why we strongly believe every manufacturer should map its journey using the Ultimo EAM Maturity Model.
The future I describe is real. And your position on that journey matters. I invite you to book a demo with Ultimo today and take our EAM Maturity Model. Every organization is on its own journey towards more mature asset management practices. Your position on that journey matters. Pinpoint where you are now, plot your path ahead, and benchmark preparedness for the 2026 frontier.
Don’t wait for disruption to force change. Let’s chart your course together - transform from reactive to smart, and build a maintenance organization that drives reliability, sustainability, and resilience in the manufacturing age.
